WHAT IS PILE FOUNDATION.
A type of deep foundation termed as pile foundation is described as a long, thin column comprised of concrete or steel that is used to support a structure and transmit loads at predefined depths using end bearing or skin friction.
When Should You Use Pile Foundation.
Following are the scenarios where adopting a pile foundation system might be useful.
- Foundation pilings seem to be the greatest choice when the groundwater table is high.
- The superstructure imposes heavy and asymmetric loads
- Other types of foundations are either too expensive or not possible.
- When the soil is compressible at a shallow depth.
- When there is a risk of scouring owing to its proximity to a river bed or the coastline, for example.
- When a canal or deep drainage system is close to the building.
- When soil excavation to the necessary depth is not feasible, due to adverse soil conditions.
- When it becomes hard to maintain the foundation trenches dry by pumping or other means because of severe seepage.
Classification Based On Functions.
Sheet Piles.
This sort of pile is typically utilised for lateral support. They often resist lateral pressure from loose soil, water flow, and so on. They are commonly used for cofferdams, trench sheeting, beach protection, and other similar applications. They are not employed to support the building vertically. They are often used for the following purposes:
- Retaining wall construction.
- River bank erosion protection.
- Keep the loose dirt surrounding the foundation trenches in place.
- For foundation separation from neighbouring soils.
- For soil confinement and hence increased soil bearing capacity.
End Bearing Piles.
Loads travel via the bottom tip of the pile in this sort of pile foundation. The bottom of the end-bearing piles is supported by a solid layer of earth or rock. The pile usually lays in the transition layer between a weak and powerful slayer. As a result, the pile serves as a column, transferring the load securely to the strong layer.
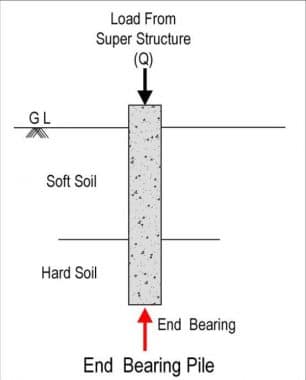
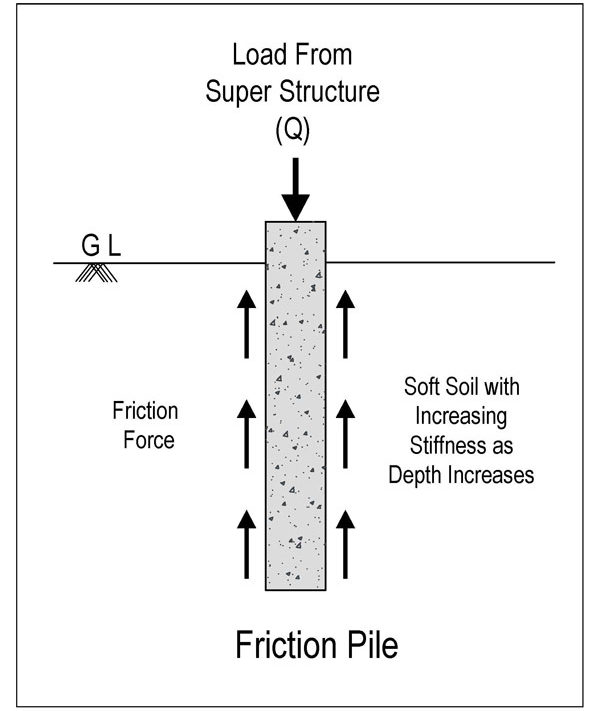
Friction Pile.
The friction pile distributes load from the structure to the earth by frictional force between the pile’s surface and the surrounding soil, such as stiff clay or sandy soil. Depending on the underlying layers, friction might occur throughout the full length of the pile or along a specific length of the pile. In general, the entire surface of the pile works to transmit loads from the structure to the earth in friction piles.
The pile’s capacity is determined by multiplying the pile’s surface area by the safe friction force created per unit area.
Pile Foundation Classification Based on Materials.
Timber Piles.
Timber piles are stacked foundations that are put beneath the sea level. They have a lifespan of roughly 30 years. They can have either a rectangular or circular form. Their diameter or size can range between 12 and 16 inches. The pile’s length is typically 20 times its top breadth.
They are typically rated for 15 to 20 tonnes. Bolting fish plates to the piles’ sides provides additional strength.
Concrete Piles.
Pre-cast Concrete Pile.
If the precast concrete pile foundation is rectangular in shape, it is cast in a pile bed in horizontal form. Circular heaps are often cast vertically. Precast piles are often strengthened with steel to avoid fracture during mobility from the casting bed to the foundation site. Curing must be conducted as specified once the piles are cast. Pre-cast piles typically require 21 to 28 days to cure.
Steel Piles.
Steel piles might be of I-section or hollow pipe construction. They are made of concrete. The diameter can range from 10 to 24 inches, while the thickness is typically 34 inches. The piles are simple to drive because to their tiny sectional area. They are mostly employed as end-bearing piles.


